-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Parjith N Goswami*, Shashank J Pandya and Hiren Patel
Corresponding Author: Parjith N Goswami MBBS, MD(Microbiology), Professor and Head-GCRI. Microbiology Laboratory, The Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute, NCH Campus- Asarwa, Ahmedabad-380016, Gujarat, India.
Received: March 20, 2021 ; Revised: April 6, 2021 ; Accepted: April 9, 2021 ; Available Online: May 26, 2021
Citation: Goswami PN, Pandya SJ & Patel H. (2021) Detection of SARs CoV-2 During Initial Phase of Pandemic from Population of Banas Kantha District of Gujarat -India with Special Emphasis on Pooled Samples. Int J Med Microbiol Immunol, 1(1): 1-7.
Copyrights: ©2021 Goswami PN, Pandya SJ & Patel H. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Abstract
Introduction: Coronavirus (SARs CoV-2) has caused an immense effect on morbidity and mortality of the population globally. We undertook this study as we are a part of one of the network laboratories of Indian Council Medical Research to test the patient’s sample by Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT PCR) for the ORF 1 ab gene of coronavirus.
Material and Method: For a period of one and half months (14th April to 31st May 2020), we tested the nasopharynx and oro-pharynx swab samples sent to us in Viral Transport Media (VTM) from the assigned districts of Gujarat. All the samples were subjected to the RT PCR method by following the standard methods.
Results: Total of 9.04% (256/2833) population was positive and 54.29% (139/256) belonged to age groups 21-40 and 25.78% (66/256) to 41-60 years. Above the age of 60 years, there were only 8.59% (22/256) cases which were positive. It was advantageous to pool the samples. Out of the number of pools prepared, we reported around 80% negative and the rest were positive in pools. The study also included association of viral load and infectivity. We found that 12% of the asymptomatic people and 5.1% of symptomatic individuals had high viral load.
Conclusion: It is seen that the detection of Novel Coronavirus -19 (SARs COV 2) by RT PCR is a reliable method and the establishment of the Ct value and infectivity of the patient to the health care workers and relatives needs to be taken care of. Also, the study presents asymptomatic patients having high viral loads being highly infective.
Keywords: Coronavirus, SARs coV-2, ORF 1ab gene, COVID-19, Ct Value
INTRODUCTION
COVID Epidemiology & Data Management Team@, COVID Laboratory Team*, VRDLN Team$.
COVID Epidemiology & Data Management Team@, COVID Laboratory Team*, VRDLN Team $ COVID Epidemiology & Data Management Team@, COVID Laboratory Team*, VRDLN Team$.
The current pandemic of upper respiratory infection and pneumonia due to Novel Coronavirus (SARS CoV-19) has caused morbidity and mortality worldwide [1]. There is well-aware fact that this respiratory disease began in China and has spread globally [2].
The Corona viruses were recognized as an independent family in 1968 and are commonly characterized by infection resembling that of the chicken respiratory virus and mouse hepatitis virus. Electron microscopic structure showed a spherical particle surrounded by a halo (Latin: Corona) of surface projections. They have a diameter of 80-200 nm and the surface is covered with bulbous projection 20nm long and 10nm wide at their distal end [3]. Corona virus invade the respiratory tract via the nose with an incubation period of 3 to 5 days & symptoms of common cold, nasal obstruction, sneezing, and running nose and occasionally cough. There are different methods for the diagnosis of coronavirus infection like viral culture, electron microscopy detection, and by ELISA test [4].
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has been leading India’s laboratory surveillance testing for COVID-19. As a part of the network laboratories of ICMR, The Microbiology Laboratory of the Gujarat Cancer and Research Institute, Ahmedabad was appointed as a nodal laboratory for testing the samples of the symptomatic patients and non-symptomatic population. Thus, we take this opportunity to generate the results of COVID-19 infection of the different categories of population under study and assess the infectivity of the virus based on the cycle threshold value (Ct value).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
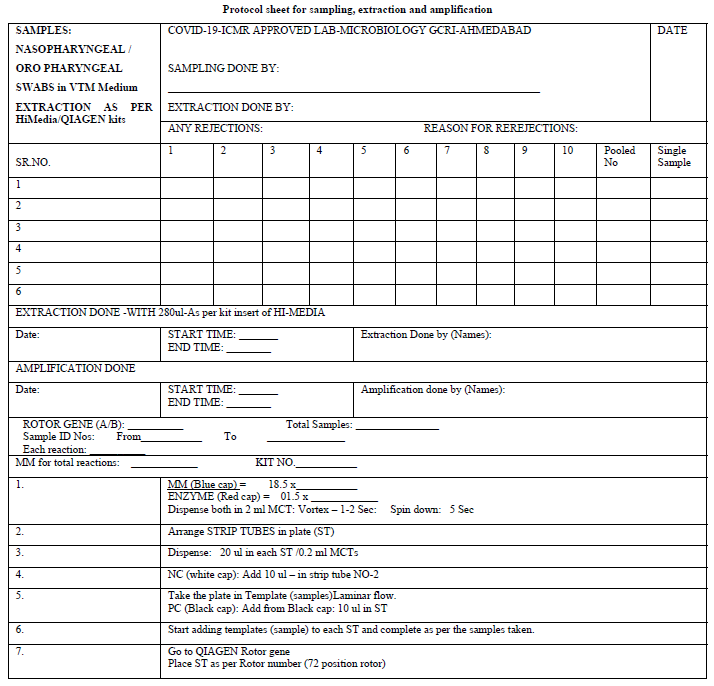
The Microbiology Laboratory (NABL accredited) of The Gujarat Cancer and Research Institute, Ahmedabad applied formally for the grant of permission to start the testing of COVID-19 from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi. After getting permission, the protocol sheets were prepared for extraction and amplification (protocol sheet). The Research and Technical staff of the GCRI were given formal training on RT PCR testing methods. The Standard Operative Procedure for laboratory safety guidelines as per ICMR were prepared and the staff was trained in using Personal Protective Equipment and other safety precautions. The study and data accumulation were carried out with the approval from the institutional review board/Committee (IRB/C).
Population Under Study
Different districts of Gujarat were allotted to us for screening and testing for COVID-19. And the nasopharyngeal / oropharyngeal samples were collected in VTM from the population. The districts allotted to us were Anand, Kheda, Mehsana, Saba kantha, Patan and Banas kantha. The population were classified into seven categories like symptomatic suspected cases, asymptomatic groups having high-risk contacts or high-risk health care workers and also asymptomatic population from green zone, as per the categories defined by ICMR portal entry forms of the population.
Method
After receiving the samples in viral transport media (VTM), the integrity of the samples was checked. They were double checked with the patient’s details with the sample referral form (SRF). The observation of any mismatch or leak of the media led to sample rejection. The laboratory testing processes started with giving proper Lab ID numbers and sampling from the VTM was performed as described by ICMR protocol such that adequate RNA was fetched from the media. For the extraction of the RNA, we used a HiGenoMB kit from Hi-Media and for amplification we used BGI kits respectively received from ICMR depot situated at NIOH, Ahmedabad. The BGI kit detects the ORF1 ab gene of COVID-19 by RT PCR. The protocols and test procedures for both were prepared and were readily made available to the staff involved in the test performance. The method given in the kit literature was followed to perform the test.
Initially the samples tested were individual. Later they were pooled into 8, 10 & 16 which were received from the green zones in successive batches. The design of the spread sheet for sampling, extraction and amplification is illustrated in the Protocol sheet.
Pooled Sampling
ICMR: Recommendations for sample pooling for real-time RT-PCR screening for COVID-19 are as follows: Advised to use only in areas with low prevalence of COVID-19 [5].
DMER-Gandhinagar: Laboratory test and pooling [6].
Throat / Nasal swabs to be collected for RT-PCR tests Sample should be tested in a one-time pool of 25. Results of this sample pooling is only for surveillance purposes. It should not be used for diagnosis of individual patients.
Method Followed by Laboratory for Pooling
Our laboratory used a pool of 8 / 10 or 16 depending upon sample size.
RESULTS
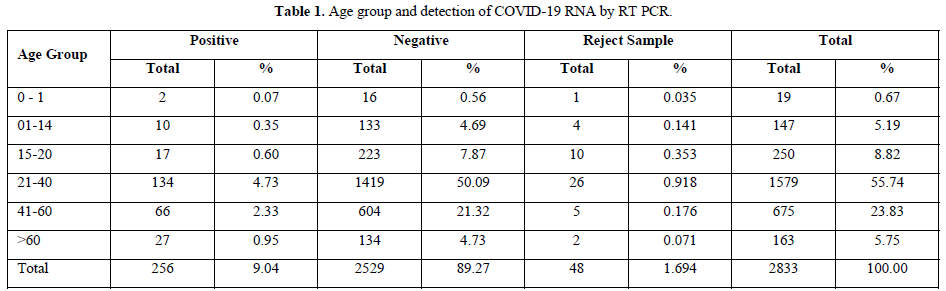
The testing was performed from 14th April to 31st May 2021 for a period of one and half months and the results were analyzed. Out of the total population of 2833, 134, 66 and 27 persons were COVID-19 positive in the age groups of 21-40 years, 41-60 years and above 60 years respectively. And 48 samples were rejected due to sample and form irregularity (Table 1).
Of the total samples tested, for whom the ICMR data was available, 33.39% (n=1692) persons were asymptomatic who were high-risk contact of confirmed cases of family members (cat.5a), and 3.37% (57/1692) were positive for coronavirus. Symptomatic contact of lab confirmed cases (cat.2) were 6.03% and 2.25% were positive, 2.78% belonged to symptomatic travelers in the last 14 days(cat.1) and 0.06% were positive. Of the hospitalized SARI patients (cat.1), 0.77% were positive and the rest were negative. Amongst the other category (48.52%), there were 4.31% (73/1692) patients positive for coronavirus infection. (Table 2).
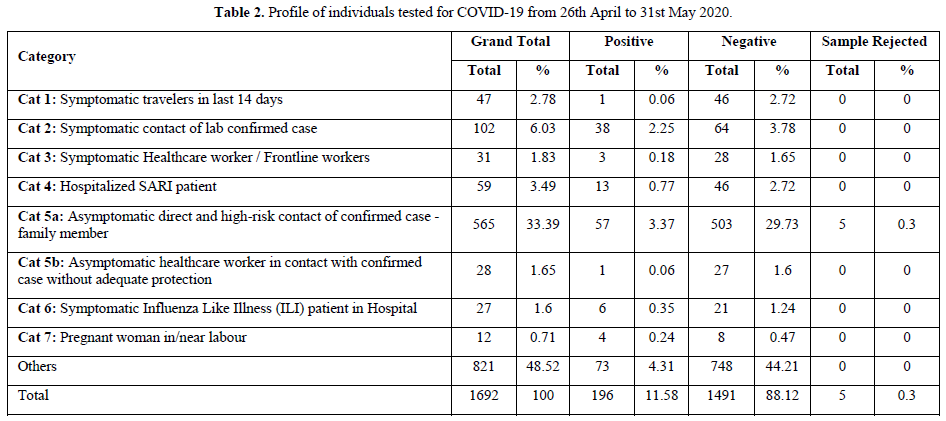
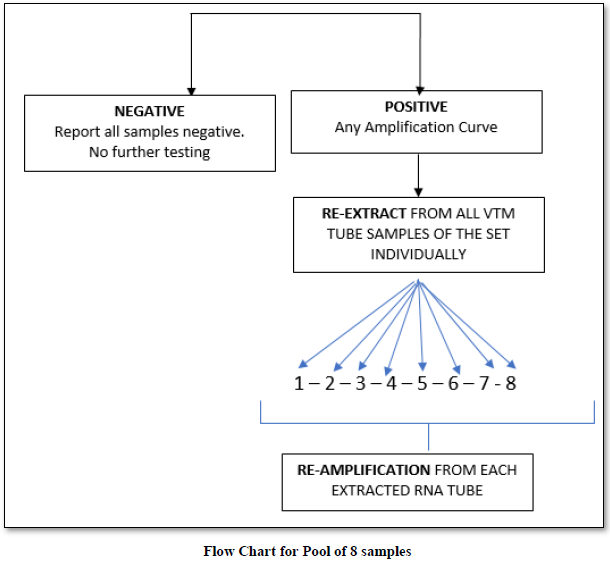
The purpose of pooled samples is to increase the capacity of the laboratories to screen increased numbers of samples using molecular testing for COVID-19 for the purpose of surveillance. Hence, it may help to use the pooled samples for screening. A pooled testing algorithm involves the PCR screening of a specimen pool comprising multiple individual patient specimens, followed by individual testing (pool deconvolution) only if a pool screens positive. As all individual samples in a negative pool are regarded as negative, it results in substantial cost savings when a large proportion of pools tests negative.
Result of Pooled Samples
On an average, we performed pooling of samples in numbers of 8,10 & 16. There were 48 pools of 8, in which 14 pools were positive and 34 were negative. In the deconvolution of these pools, 14 pooled samples (112/384 individual samples) were further subjected to re-extraction and re-amplification. There were 11% positive and 89% were negative. Next, there were 31 pools of 10, in which only 2 pools were positive and 29 were negative. Out of these 2 pools (20/310 samples) 0.64% (2 samples) were positive while deconvoluting 99.35% were negative. Similarly, 32 pools of 16 samples showed 7.42% positive and 92.58% were negative (Figure 1).
Importance of Ct Value
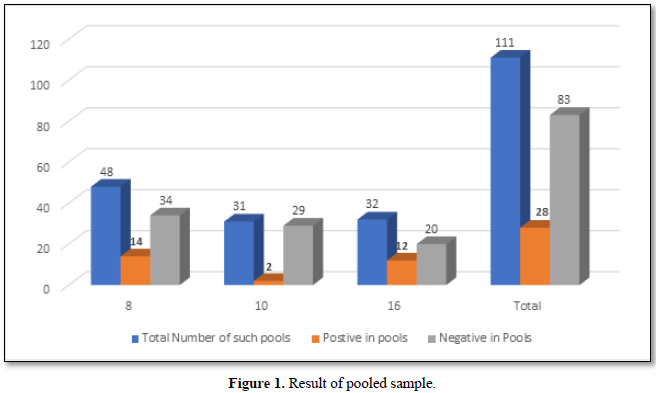
The Ct (cycle threshold) is the number of cycles required for the fluorescent signal to cross the threshold (i.e., exceeds background level). Ct levels are inversely proportional to the amount of target nucleic acid in the sample (i.e., the lower the Ct level the greater the amount of target nucleic acid in the reaction (Figure 2).
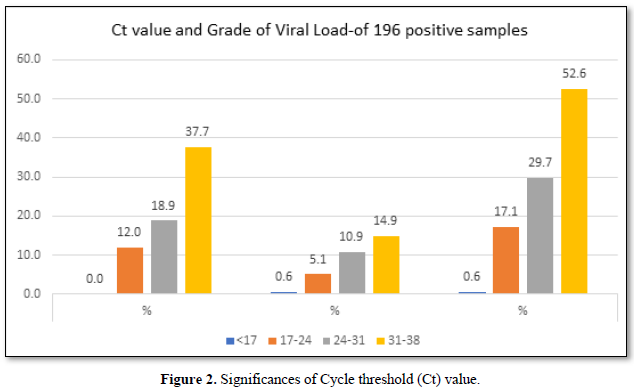
The viral load is classified based on the Ct (cycle threshold) value of the amplification of the Coronavirus RNA in the reaction of RT PCR. As per Figure 3, the categories are 17-24 Ct as high viral load, 24-31 as moderate viral load and 31-38 as low viral load. Of the 175 selected positive person’s samples, 12% of the asymptomatic people had higher viral load,18.9% had moderate viral load and 37.7% had low viral load. Whereas in symptomatic patients, 5.1% had high viral load, 10.9 % had moderate and 14.9% had low viral load. In total 17.1% had high viral load and 29.7 had moderate viral load and 52.6% were having low viral load.
DISCUSSION
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by SARS-Cov-2 was the first reported in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China in late December 2019.
During the current coronavirus pandemic, the testing done by RT-PCR for the Orf gene detection for a period of one and half month showed 9.04 % of the cases were positive. The reports of COVID-19 positive by Wen-Hua Kong [7] and the reports of ICMR study group showed the positivity of 10.6% in Maharashtra, 7.8% in Delhi, 6.1% Madhya Pradesh & 5.8% West Bengal.
Contrary to the reports published by other workers, we found highest detection of coronavirus RNA in age groups 21-40 and 41-60 years which is 4.73% & 2.33% respectively, but it was only 0.95% in >60 years of age.
Many cases whose samples were collected (33.3%) belonged to asymptomatic high-risk contact of confirmed family member and the detection of corona RNA was 3.73% Which is similar to the report published by ICMR study group for reasons unknown, the detection of the virus was less (2.25%) in symptomatic contact of laboratory confirm case & symptomatic travelers (2.78%) [8].
To avoid dealing with the large number of sample loads received from districts for COVID-19 testing, we pooled the samples. Pooling the samples lessened the burden of work with limited staff and economizing on the reagents. This has been beneficial in samples received from green zones or areas where the incidence of infection is <5%. We found 11%, 0.64% and 7% detection of COVID-19 from 8, 10 and 16 pooled samples. During the literature search we could not find any such results with other studies if at all done for comparison.
In a press release in The Times of India 3rd June 2020, the Ahmedabad based ICMR- National Institute of Occupational Health (NIOH), studies 2000 individuals of which 140 were COVID-19 positive (7%). They concluded that infected patients do not transmit the virus uniformly. They observed that infected cases bearing high viral load spread the infection at a rate almost eight times higher than cases with low viral load. In their study of the 140 positive cases, those with high viral load were limited to only 7% of the infected population, and 9% had moderate viral load and 84% had low viral load. Unlike their report, we found 17.1% patients with high viral load, 29.7% with moderate viral load and 52.6% having low viral load. Further in addition to the above, we found that the high viral load was more (12%) in asymptomatic patients than when compared with symptomatic patients (5.1%). Another study in China showed that probably only 10% of the population with high viral load spread 80% of the infection.
CONCLUSION
The current Coronavirus disease pandemic caused by SARS-CoV2 viruses was reported first from China in December 2019 and has already engulfed the world. A high number of COVID-19 test confirmed cases account for 84% in 10 states of India. Gujarat reported more than 20,000 confirmed cases. Our study showed around 9% confirmed cases. Based on the Ct value, the high and moderate viral load patients should be isolated and hospitalized on priority. Those with low viral load should take all precautions for containing the disease. Moreover, health care professionals at COVID-19 hospitals are exposed to patients with high viral load and are prone to get infected. Therefore, they should take necessary precautions to protect themselves.
REFERENCES
Share Your Publication :